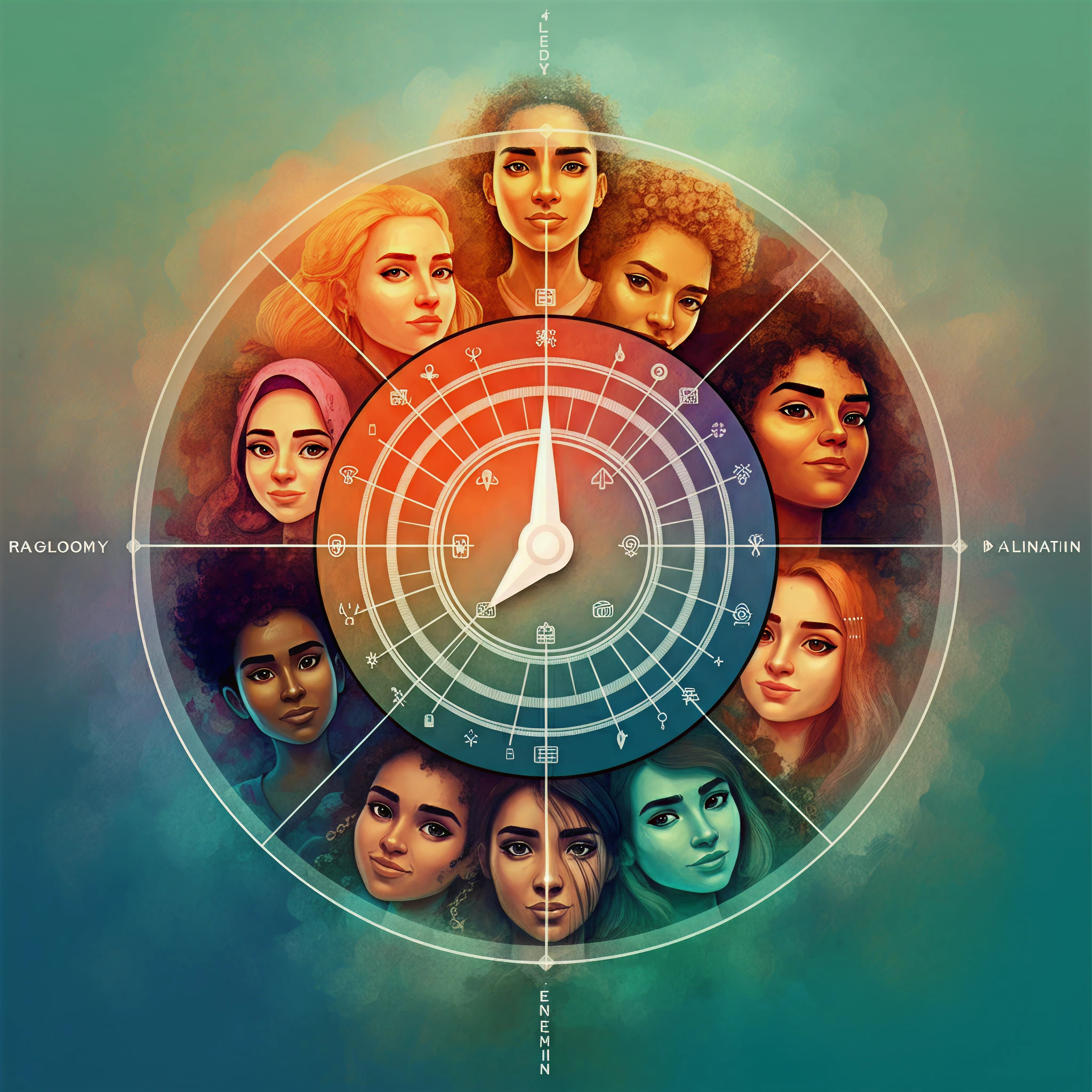
What is the Intersectionality Wheel?
The “Intersectionality Wheel” is a visual framework that helps us understand how different aspects of our social and personal identities intersect and contribute to privilege, disadvantage, and marginalization. Coined by Kimberlé Crenshaw, intersectionality highlights how systems of oppression (e.g., sexism, racism, ableism) overlap, creating complex and unique experiences for individuals. The Intersectionality Wheel represents these intersections in a tangible, accessible way, enabling advocates, professionals, and students to analyze and address inequalities on both individual and systemic levels.
Key Dimensions Represented on the Wheel
The Intersectionality Wheel is divided into several “axes” or dimensions, representing the layered and multifaceted aspects of identity. Typically, these include:
- Race/Ethnicity
- Gender Identity and Expression
- Sexual Orientation
- Social Class and Economic Status
- Ability/Disability
- Age
- Religion
- Education
- Citizenship or Immigration Status
Each dimension influences a person’s lived experience. These factors do not operate in isolation but intersect in varied ways, amplifying privilege or exacerbating oppression.
For example, consider the experiences of a Black woman who uses a wheelchair. She may face racism, sexism, and ableism simultaneously, shaping her unique challenges compared to others who may share only one or two of these identities.
How to Use the Intersectionality Wheel
1. Explore Individual Identities
The Intersectionality Wheel can be used as a self-reflection tool by identifying where an individual’s identities fall on each axis. This highlights areas of privilege or marginalization based on their specific combinations.
2. Analyze Group Dynamics
Organizations can use the Wheel to assess inclusivity within their teams or communities. By analyzing overlapping dimensions, they can pinpoint where barriers may exist for certain groups.
3. Develop Equity Strategies
The Wheel provides a guide for creating equity-based policies. By accounting for diverse, intersecting identities, businesses and institutions can develop strategies to address the unique challenges faced by marginalized groups.
For example:
- A workplace developing a family leave policy might consider the specific needs of single parents, LGBTQ+ parents, and parents with disabilities, ensuring no group is unintentionally excluded.
Benefits of Using the Intersectionality Wheel
- Raises Awareness: Encourages understanding of how overlapping identities shape power dynamics.
- Drives Inclusive Decision-Making: Enables organizations to create more equitable systems and policies.
- Promotes Social Justice Work: Helps address systemic inequalities in a targeted and meaningful way.
Limitations and Criticisms
While the Intersectionality Wheel is a powerful tool, it is not without its challenges:
- Oversimplification: Reducing complex identities into segmented dimensions can oversimplify lived experiences.
- Implementation Challenges: Without the right tools or understanding, the framework may be misapplied or tokenized.
- Subjectivity of Interpretation: Different people may interpret where they fit on the Wheel differently, adding complexity to its analysis.
Addressing these limitations requires ongoing education, reflection, and adaptation in real-world applications.
Examples of Real-World Applications
1. Human Resources
HR teams can use the Intersectionality Wheel to evaluate hiring processes, ensuring that marginalized identities are not inadvertently excluded due to implicit bias.
2. Education
Educators can utilize the framework to develop more inclusive curricula that reflect diverse histories, cultures, and experiences.
3. Healthcare
Healthcare providers can use the Wheel to identify barriers to care for populations that face systemic inequalities, such as LGBTQ+ individuals or low-income families.
4. Marketing and Branding
Businesses can apply the framework to create messaging that resonates with multiple, intersecting identities, ensuring inclusivity in campaigns.
Resources for Further Learning
If you’re interested in exploring the concept of intersectionality and the Wheel further, check out these resources:
- Books: “Intersectionality” by Kimberlé Crenshaw and “Sister Outsider” by Audre Lorde
- Workshops: Seek out DEI training that incorporates intersectionality into organizational practices.
- Online Tools: Interactive intersectionality frameworks, which allow users to visualize how their identities intersect.
Final Thoughts
The Intersectionality Wheel is a vital framework for anyone working in social justice, DEI, academia, or policy-making. It challenges us to think beyond single-axis perspectives and inspires holistic, inclusive approaches to addressing inequality. By incorporating this tool into your work, you’ll be better equipped to empower individuals, advocate for change, and create a more equitable society.
Looking to deepen your understanding or apply the Intersectionality Wheel in your efforts? Contact our expert team for customized training and resources to help your organization thrive. Together, we can build a more inclusiv