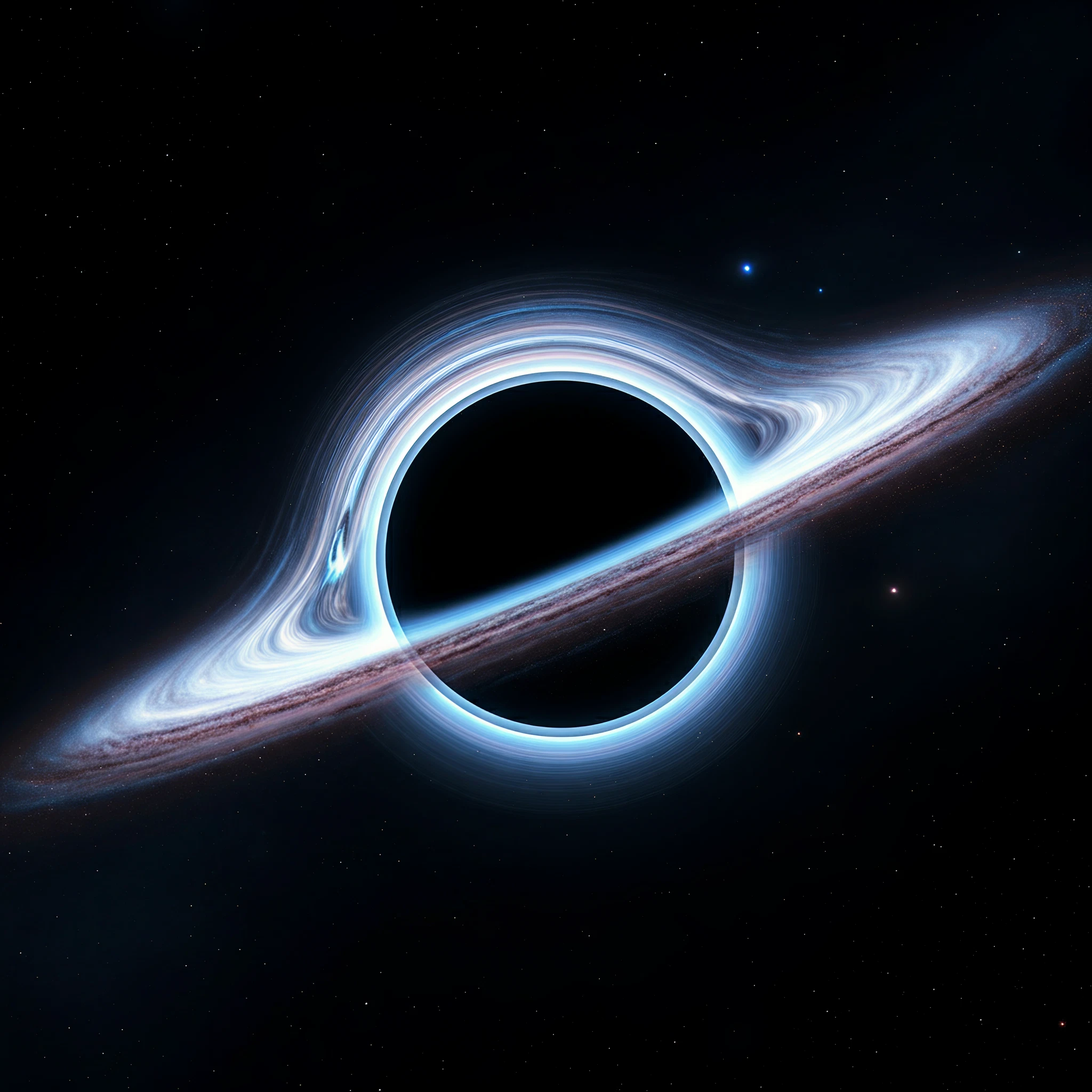
Black holes have always been the objects of fascination in the universe. Their immense gravitational power makes them one of the most mysterious and captivating phenomena in astrophysics. And now, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled a groundbreaking discovery that reshapes our understanding of black hole behavior and galactic evolution.
Astronomers have identified a rogue black hole, roughly 20 million times the mass of our Sun, wandering across space and leaving a trail of newly formed stars in its wake. This finding is not only an incredible scientific milestone but also paints an awe-inspiring picture of the dynamics at play within galaxies.
A Black Hole on the Run
Most supermassive black holes are typically found at the centers of galaxies, anchoring everything around them with their colossal gravitational pull. But this black hole is different. It’s roaming freely within a galaxy, located approximately 600 million light-years away from Earth. Imagine a cosmic predator, moving silently through the expansive darkness of the universe, devouring anything that crosses its path.
Hubble’s observations revealed that this massive black hole is not an invisible void of destruction but rather a beacon of creation. Its passage compresses gases in such a way that it sparks new star formation. Essentially, this “monster” black hole is both consuming and creating, leaving behind a celestial trail of stars that spans an astonishing 200,000 light-years. For comparison, that’s twice the diameter of our Milky Way galaxy.
Pinpointing the Discovery
The wandering black hole came to light when Hubble detected a rare phenomenon known as a “tidal disruption event” (TDE). This event occurs when a star ventures too close to a black hole and is mercilessly torn apart by its immense gravitational forces, an astronomical process often compared to “spaghettification.” The stellar material forms a disk around the black hole, emitting bursts of radiation that can be observed across vast cosmic distances.
The Zwicky Transient Facility at Caltech’s Palomar Observatory first detected this eruption of light. Further observations by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Very Large Array telescope confirmed that the flare was offset from the core of the black hole’s host galaxy. Hubble then stepped in, using its unparalleled optical precision and ultraviolet imaging capabilities, to pinpoint the exact location and trajectory of the rogue black hole.
Why Is This Black Hole Roaming?
The discovery raises new questions about how such black holes end up “adrift.” One plausible explanation involves galaxy mergers. When galaxies collide, their central black holes may interact gravitationally, sometimes ejecting one black hole into a wandering state. Another theory suggests that three-body interactions between multiple black holes may lead to one being cast out of its central position.
Interestingly, this particular black hole coexists with another, larger supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s center, which is estimated to be 100 million times the mass of the Sun. Despite being in the same galaxy, these two black holes are not gravitationally bound and exist independently, defying expectations.
A Trailblazing Insight into Galactic Evolution
This discovery sheds light not just on black holes but also on the processes governing galactic evolution. The rogue black hole’s ability to trigger star formation provides valuable insight into how galaxies evolve and how black holes influence their environments.
It also highlights the potential for finding more wandering black holes in future celestial surveys. Yuhan Yao, the lead study author from the University of California at Berkeley, noted that this is the first-ever offset TDE captured and that it opens up possibilities for uncovering an elusive population of these roaming cosmic giants.
Pushing the Boundaries of Space Exploration
This discovery by Hubble validates the importance of space telescopes in probing the mysteries of the cosmos. It demonstrates how advanced observational tools can capture fleeting yet significant events, offering glimpses into phenomena occurring hundreds of millions of light-years away.
Every discovery about black holes brings us closer to unraveling the major questions of astrophysics. How do galaxies form and evolve? How do black holes interact with their cosmic surroundings? And just how much of the universe is influenced by their omnipresent gravity?
Hubble’s findings serve as a reminder that space exploration isn’t just about documenting the vastness of the universe. It’s about uncovering stories buried within starlight, peering into the past, and paving the way for future discoveries that redefine our understanding of existence.
The Takeaway
The discovery of a roaming black hole by Hubble is a major leap in astrophysics, providing fresh knowledge about black holes, their behavior, and their role in galactic evolution. For science enthusiasts and space aficionados, this is a moment to revel in the breathtaking intricacies of our universe.
Stay tuned for more updates as we continue exploring the cosmos, and if this discovery sparked your curiosity, don’t forget to share this with fellow space enthusiasts! The universe holds unending wonders, and we’re only scratching the surface.