Taking care of your car’s battery is essential for ensuring smooth rides and avoiding the dreaded situation where your car won’t start. One of the simplest ways to monitor your car battery’s health is by checking its voltage. But you may wonder, how many volts should a car battery read? Here’s everything you need to know to maintain your car’s battery and keep it in optimal condition.
Understanding Car Battery Voltage: What’s Normal?
A car battery’s voltage tells you about its state of charge and overall health. Here’s a quick overview of what “normal” voltage readings look like:
- Fully charged car battery: 12.6 to 12.8 volts (at rest, without the engine running).
- When the engine is running: 13.7 to 14.7 volts. This higher range happens because the alternator is actively charging the battery.
If the voltage drops below 12.4 volts when the engine isn’t running, your battery’s charge is likely insufficient. Anything significantly above or below these ranges could signal a problem with your battery or charging system.
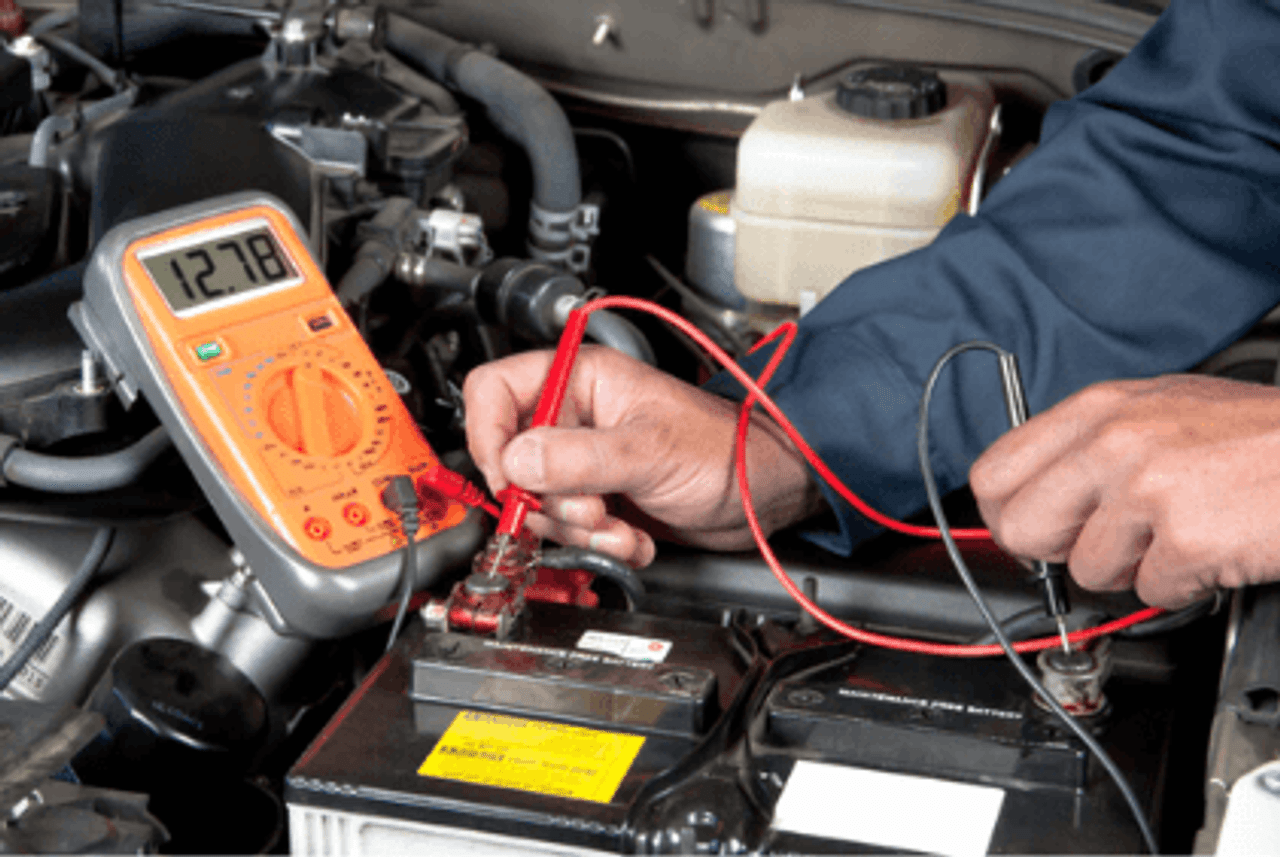
How to Measure Car Battery Voltage
Checking your car battery voltage is a straightforward task that you can do with a multimeter. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get an accurate reading:
- Turn off your car: Ensure the engine and all electrical components (e.g., headlights, radio) are turned off.
- Set your multimeter: Adjust your multimeter to measure DC voltage (denoted as “V” with a solid and dashed line above it).
- Connect the probes:
-
-
- Attach the red probe to the positive terminal (+) on the battery.
- Attach the black probe to the negative terminal (-).
-
- Read the display: The multimeter will display the battery voltage. Compare the reading to the normal voltage ranges listed above.
- Take additional readings if needed: To get a full picture, measure the voltage while the car is running to check the alternator’s performance.
Factors Affecting Car Battery Voltage
A car battery’s voltage isn’t static and can fluctuate due to several factors. Here’s what you should keep in mind:
- Temperature: Extreme cold or heat can lower your battery’s voltage. Cold weather especially reduces your battery’s starting power.
- Age: Over time, batteries naturally lose their ability to hold a charge. Even a well-maintained battery will typically last 3–5 years.
- Usage patterns: Consistently short trips, leaving lights or electronics on, or a parasitic drain (when components pull power while the car is off) can reduce your battery voltage.
Interpreting Voltage Readings
When you measure your car battery voltage, the numbers can provide clues about its health:
- 12.6+ volts (engine off) – Great! Your battery is fully charged.
- 12.4–12.6 volts (engine off) – Okay. Your battery is partially charged but could use a jump or recharge soon.
- Less than 12.4 volts (engine off) – Your battery may be weak or discharging. Consider recharging it and monitoring future readings.
- Above 14.7 volts (engine running) – This could indicate your alternator is overcharging the battery, which can cause damage.
Troubleshooting Low Voltage
Have you noticed your battery voltage dropping below normal levels? Here are some common causes and solutions:
- Dirty battery terminals:
-
-
- Dirt and corrosion can create resistance, interfering with the battery’s power delivery.
- Solution: Clean the terminals using a mixture of baking soda and water with a wire brush.
-
- Parasitic drain:
-
-
- Some components in your car may be drawing power when the vehicle is off.
- Solution: Have a mechanic inspect your car’s electrical system.
-
- Faulty alternator:
-
-
- If your alternator isn’t charging your battery properly, your voltage will drop.
- Solution: Test your alternator and replace it if necessary.
-
- Battery nearing the end of its lifespan:
-
-
- If your battery is 4+ years old, it might not hold a charge properly.
- Solution: Replace the battery.
-
Maintaining Optimal Car Battery Voltage
To ensure your car battery stays healthy and functional, follow these tips:
- Drive regularly:
-
- If your car sits idle for long periods, the battery may discharge. Aim for at least one longer drive each week.
-
- Turn off electrical components:
-
- Always make sure your headlights and interior lights are turned off when exiting your vehicle.
-
- Check the terminals:
-
- Regularly inspect and clean the battery terminals to prevent corrosion.
-
- Monitor voltage periodically:
-
- Check your battery’s voltage every few months using a multimeter, especially before long trips.
-
- Invest in a battery maintainer:
-
- If you don’t drive often, a battery maintainer (trickle charger) can keep your battery charged without overcharging.
-
Final Thoughts
Knowing how many volts a car battery should read gives you valuable insight into your vehicle’s health. A properly maintained battery ensures reliable starts, prevents unexpected breakdowns, and extends the life of your car’s electrical system.
Stay ahead of battery issues by routinely checking its voltage and addressing any warning signs promptly. With a bit of proactive care, you’ll keep your battery in top condition for years to come!