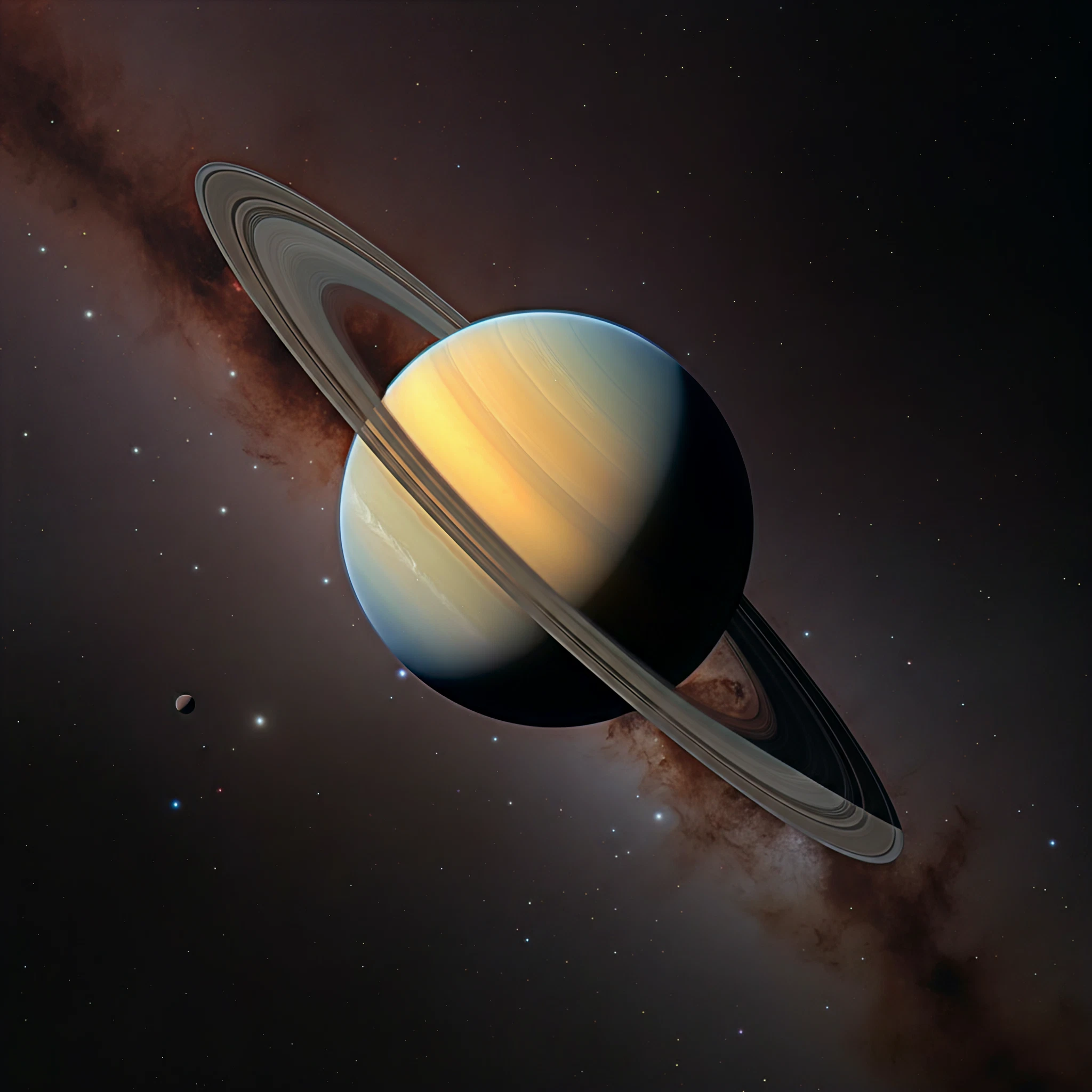
Saturn, the captivating gas giant adorned with its signature rings, is a world of extremes. Its breathtaking beauty hides a tumultuous and dynamic climate shaped by unique atmospheric phenomena, fierce winds, and seasonal transformations. Whether you’re a student, a science enthusiast, or a general reader, unraveling the mysteries of Saturn’s climate offers a fascinating glimpse into the challenges and wonders of our universe.
Saturn’s Atmosphere and Weather Patterns
Saturn’s atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen (about 96%) and helium (around 3%), with traces of methane, ammonia, water vapor, and other compounds. Beneath its serene, golden clouds lies a world of turbulence and extreme weather patterns driven by both internal heat and solar energy.
One of Saturn’s most striking features is its equatorial jet stream, with wind speeds reaching up to an astonishing 1,600 km/h (994 mph). These supersonic winds are among the fastest in the solar system, creating a climate of perpetual motion. The planet also boasts frequent storms and massive atmospheric disturbances, including the infamous Great White Spot, a periodic storm system that dwarfs any storm we’re familiar with on Earth.
Seasonal Variations on Saturn
Unlike Earth, where seasons change approximately every three months, Saturn’s seasons last about seven Earth years each due to its lengthy 29.5-year orbital period around the Sun. These seasons profoundly impact its atmospheric dynamics and cloud formations.
The tilt of Saturn’s axis (about 27 degrees, similar to Earth’s 23.5 degrees) means that as it orbits the Sun, different hemispheres experience varying levels of solar radiation. This seasonal tilt influences temperature distributions and wind patterns, contributing to distinct changes in Saturn’s appearance and climate over time.
Prominent Features of Saturn’s Climate
Saturn’s climate is marked by unique and dramatic phenomena:
- The Great White Spot
This colossal storm emerges roughly every 30 years during Saturn’s northern hemisphere summer, creating a bright, white band visible even from Earth. It is a result of pent-up atmospheric energy being released in dramatic fashion.
- Jet Streams and Bands
Saturn’s bands, composed of alternating light and dark layers, are driven by its strong jet streams. They create the beautifully striped appearance we see in its atmosphere.
- Hexagonal Polar Vortex
At Saturn’s north pole lies a bizarre, six-sided jet stream spanning nearly 30,000 km (18,600 miles). This hexagon has puzzled scientists for decades and remains a unique feature of Saturn.
How Saturn Compares to Other Gas Giants
While all gas giants exhibit turbulent atmospheres, Saturn’s climate has unique characteristics that set it apart. For example, Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, though similar to Saturn’s Great White Spot, is a long-lasting feature, whereas Saturn’s storms are more transient. Additionally, Saturn’s wind speeds surpass those of Jupiter, giving it some of the fastest-moving atmospheric phenomena in the solar system.
The Role of Saturn’s Rings
Saturn’s iconic rings do more than just add to its beauty; they also influence its climate. Composed of ice particles and rocky debris, the rings cast shadows on the planet’s atmosphere, cooling certain regions. This cooling can amplify temperature contrasts and lead to unexpected weather patterns, such as localized jets or storms.
Recent Observations and Research
Ongoing missions like NASA’s Cassini spacecraft have provided groundbreaking insights into Saturn’s climate. These observations have revealed intricate details about its storm dynamics, cloud chemistry, and polar features, significantly enhancing our understanding of this gas giant.
Additionally, researchers continue to study the heat generated from Saturn’s interior, which significantly influences its weather patterns. Unlike Earth, where sunlight is the primary source of atmospheric energy, Saturn’s internal heat contributes as much as 80% of its atmospheric dynamics.
Speculating About Climate Change on Saturn
While “climate change” on Saturn differs greatly from that on Earth, its weather is far from static. Seasonal shifts, internal processes, and the influence of its rings constantly shape the planet’s atmosphere. Understanding these dynamics can provide valuable perspectives for studying planetary weather systems, including those closer to home.
Conclusion
The climate of Saturn is as enigmatic as the planet itself, characterized by extreme winds, awe-inspiring storms, and intriguing atmospheric phenomena. Its unique combination of internal heat and solar influence offers a dynamic and evolving environment that continues to fascinate scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Exploration and research into Saturn’s climate not only deepen our understanding of this magnificent gas giant but also enrich our knowledge of planetary sciences as a whole. To witness such an extraordinary interplay of forces is to appreciate the vast complexity of our universe.
Are you curious to learn more? Engage with the wonders of planetary science and explore the boundless possibilities of our solar system’s giant worlds!