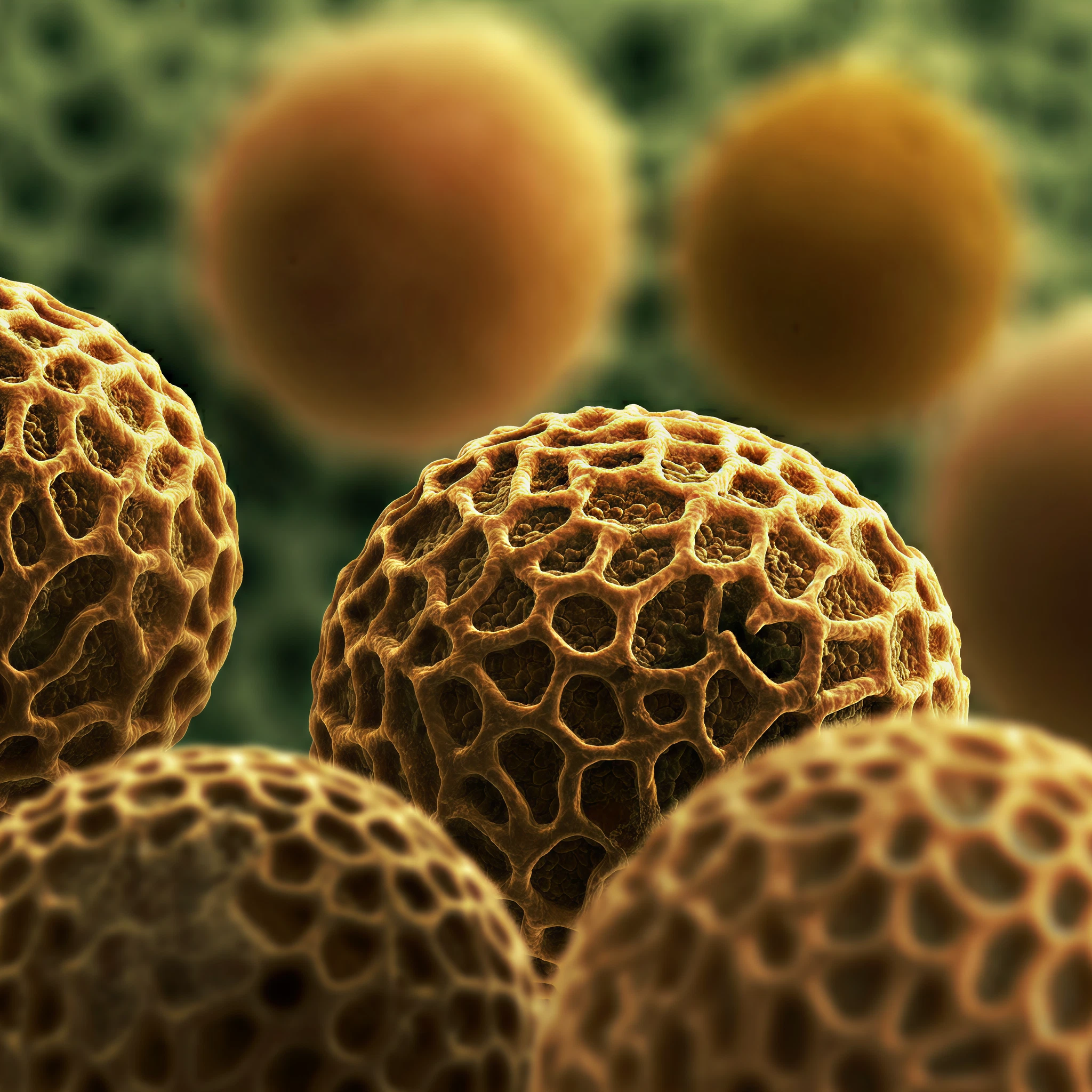
Nature often preserves its secrets in surprising ways, and ancient pollen is a perfect example of this. These microscopic grains, hardy enough to withstand the test of time, serve as nature’s time capsules. For history enthusiasts and researchers alike, pollen offers a remarkable window into our world’s forgotten past, revealing invaluable insights into ancient climates, agriculture, ecosystems, and even human migrations.
Nature’s Time Capsules
Pollen grains are a unique way to glimpse the planet’s history. Their tough outer shells enable them to survive long after the plants that produced them are gone. Trapped in the sediments of lakes, oceans, and riverbeds, fossilized pollen creates a timeline of Earth’s natural transformations, recording shifts in vegetation, climate, and human activity over the millennia.
What Ancient Pollen Reveals
Past Climate Changes and Vegetation
Ancient pollen provides critical evidence of how climate shapes life on Earth. Long-term pollen studies have documented dramatic shifts in vegetation during periods like the Ice Age or Medieval Warm Period. For instance, regions that are now arid deserts once flourished with lush forests, as evidenced by pollen deposits found buried beneath layers of earth. By tracing these changes, scientists can better understand how ecosystems adapt to evolving climates.
Historical Agricultural Practices
We think of agriculture as humanity’s way of shaping the landscape, but pollen tells us how farming has shaped our history. Pollen studies reveal when and where certain crops were first cultivated, such as wheat in Mesopotamia or maize in Central America. They also trace the rise of ancient farming societies and their growing dominance over hunter-gatherer populations, a pivotal moment in human history.
The Spread and Decline of Plant Species
Pollen doesn’t just document the presence of plants; it tells their stories of survival and extinction. By analyzing declining pollen counts, researchers have reconstructed detailed accounts of deforestation and land overuse in areas like the Amazon Basin or Europe during industrial booms.
Human Migrations and Land Use
Pollen records often act as silent witnesses to human movement. When populations relocate, they bring with them seeds and farming techniques that leave a trail of pollen in their wake. These patterns help researchers understand ancient migration routes, settlement patterns, and land-use changes across continents.
How Pollen Inspires Modern Applications
The study of pollen, known as palynology, isn’t just about looking at the past. The data also informs modern practices:
- Climate Forecasting: Understanding past climate trends allows scientists to predict future shifts and their potential impact on ecosystems.
- Conservation Efforts: By uncovering which environments thrived in historical climates, researchers can make more informed decisions about restoration projects.
- Agricultural Innovation: Ancient crop data aids in developing resilient farming practices by identifying species that thrived under similar conditions in the past.
Why Ancient Pollen Matters Today
For history enthusiasts, pollen analysis is more than a science; it’s a treasure map leading to forgotten stories of Earth’s past. By connecting the dots between climate, agriculture, and human activity, this tiny grain highlights the intricate ways nature and humanity have shaped one another through time.
Researchers continue to unearth startling new insights, proving that even the smallest relics of our past can hold the weight of vast historical narratives. The study of ancient pollen isn’t just about looking back at what was; it’s about envisioning what could be, learning from the past to guide the decisions of our future.
Want to dig deeper into the history locked within the natural world? Explore resources available through paleobotanical research centers or join local workshops on palynology to uncover the hidden stories waiting in grains of pollen.
Images to Include
- Microscopic view of pollen grains
- Caption: “A close-up of pollen grains from various plants, showcasing their intricate structures. Pollen’s durability as a time capsule lies in these tough outer shells.”
- Visual timeline of vegetation change
- Caption: “Pollen analysis reveals how dense forests once blanketed regions now transformed into arid deserts.”
- Map of historical crop origins
- Caption: “Pollen records indicate where staple crops like wheat and maize were first cultivated, reshaping human history.”
- Illustration of human migrations with overlapping vegetation maps
- Caption: “Pollen trails help researchers track ancient human migrations and the spread of agricultural practices over time.”
By understanding ancient pollen, we gain far more than facts—we uncover stories of resilience, adaptation, and transformation that continue to shape our world today.