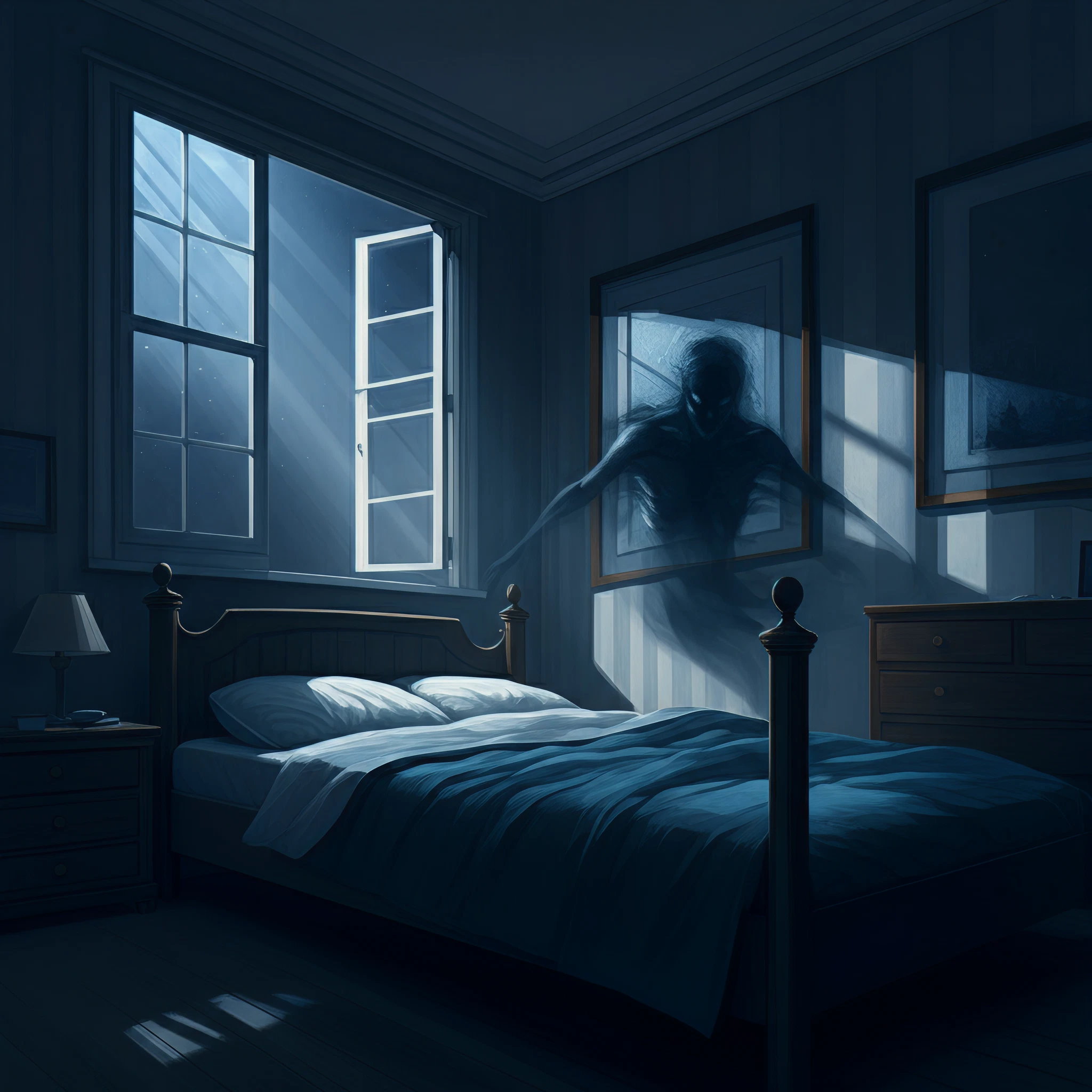
Sleep paralysis is a fascinating and sometimes frightening phenomenon. For years, it has been the subject of folklore, art, and even horror films, often described as the moment when shadowy figures or otherworldly entities seem to emerge in the dead of night. These vivid hallucinations are commonly referred to as “sleep demons.” But what is sleep paralysis, and how much of it is grounded in science versus cultural interpretation? Let’s explore.
What Is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis occurs when your brain is awake, but your body remains immobilized in a state of muscle atonia. This can happen during the transitional phases of sleep, either as you’re falling asleep or waking up, particularly during the REM (rapid eye movement) sleep cycle. REM sleep is essential for cognitive functions like memory and mood regulation but is also the stage where the most vivid dreaming occurs.
During these episodes, the individual’s body remains paralyzed to prevent them from physically acting out their dreams. However, when the brain “wakes up” prematurely, the body fails to follow suit, leading to a surreal state where you feel paralyzed yet fully conscious. This state often comes with intense hallucinations and a sense of dread.
Cultural Interpretations of Sleep Demons
Across the globe, people have tried to make sense of sleep paralysis through folklore and superstition. Here are some examples of how different cultures interpret these experiences:
- Western Beliefs: Figures like witches, ghosts, and other phantoms are common in Western accounts. These entities are often depicted as sitting on the chest, rendering the individual unable to breathe or move.
- Middle Eastern Folklore: The djinn, a supernatural creature in Islamic culture, is thought to explain these episodes with its ability to straddle the border between the physical and metaphysical worlds.
- Japanese Culture: Known as kanashibari, sleep paralysis is sometimes explained as a vengeful spirit paralyzing its victims.
- Scandinavian Mythology: The notion of the Mara, a malicious entity that rides on people’s chests while they sleep, is a common theme.
While many of these interpretations are culturally specific, they all reflect the terrifying nature of sleep paralysis experiences.
Common Hallucinations During Sleep Paralysis
For those who experience sleep paralysis, the hallucinations can range from unsettling to outright terrifying. The three most common types of hallucinations include:
- Visual Hallucinations – Shadowy figures, grotesque faces, or vivid imagery floating in the room.
- Auditory Hallucinations – Hearing footsteps, whispered voices, or other sounds that feel incredibly real yet inexplicable.
- Tactile Hallucinations – Feeling pressure on the chest or the sensation of being physically touched or manipulated by an unseen force.
Despite the vividness of these events, they are the brain’s response to a mismatch in sensory processing during this transitional sleep state.
Psychological Factors Behind Sleep Paralysis
While the core mechanism behind sleep paralysis lies within the sleep-wake cycle, certain psychological factors can make episodes more frequent or severe:
- Stress and Anxiety: Elevated stress levels can contribute to disrupted sleep patterns, making sleep paralysis more likely.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like insomnia or narcolepsy increase susceptibility to sleep paralysis.
- Trauma: PTSD and other psychological stressors can also heighten the frequency of episodes.
- Sleep Deprivation: A lack of restful sleep is a significant risk factor. Disrupted REM sleep cycles increase the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Coping Strategies for Sleep Paralysis
The good news is that sleep paralysis, while unsettling, is not dangerous. Here are some practical ways to reduce and manage episodes:
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Sleep regularity can stabilize your REM cycles and reduce the likelihood of disruptions.
- Improve Sleep Hygiene:
- Avoid screens before bedtime.
- Develop a relaxing pre-sleep routine.
- Ensure your sleep environment is cool, quiet, and comfortable.
- Manage Stress:
- Practice mindfulness meditation or progressive muscle relaxation to reduce anxiety levels.
- Seek professional help if stress or trauma persists.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limiting caffeine and alcohol, particularly in the hours before bed, can improve sleep quality.
For those who experience frequent episodes, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) specifically tailored for sleep disorders can be effective. Additionally, some medications can be prescribed in severe cases to regulate REM sleep.
When to Seek Professional Help
While occasional sleep paralysis is common and harmless, frequent and distressing episodes could point to an underlying issue. You should consult a healthcare professional if:
- Episodes occur multiple times a week and impact your overall well-being.
- Sleep paralysis is accompanied by other symptoms like excessive daytime sleepiness, which may indicate a sleep disorder like narcolepsy.
- You feel significant anxiety or fear around falling asleep due to frequent episodes.
Sleep specialists can conduct assessments and provide tailored treatment plans to help alleviate the condition.
Reassurance to Those Experiencing Sleep Paralysis
If you’ve experienced sleep paralysis, you’re not alone. Roughly 30% of people globally will encounter it at least once in their lifetime. While the hallucinations may feel vivid and even overwhelming, understanding the science behind them can be empowering. With the right strategies and a better understanding of what’s happening, you can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes.
Sleep paralysis doesn’t need to be a source of fear. By addressing the root causes and practicing good sleep hygiene, you can take control of your sleep and leave those “sleep demons” behind.
Sweet dreams and restful nights!
For more health articles like this, visit CNN Health. Keep learning about sleep science and discover tools to improve the quality of your nights!